Health
Rare ‘No-Burp Syndrome’ Gains Attention, But Treatment Remains Costly
A rare condition known as retrograde cricopharyngeal dysfunction (R-CPD), or “no-burp syndrome,” is gaining attention on social media, with medical specialists and affected individuals raising awareness about its impact. Despite growing recognition, treatment options remain expensive and largely inaccessible.
For many individuals, burping is a routine bodily function, but for those with R-CPD, it is impossible. The condition, formally identified in 2019 by Dr. Robert Bastian of the Bastian Voice Institute, prevents the cricopharyngeus muscle in the upper esophagus from relaxing, trapping air in the digestive system. This results in painful bloating, gurgling sounds in the throat, and severe discomfort.
Dulcie, a 23-year-old research student from the UK, experienced these symptoms for years without understanding the cause. “Now I know what R-CPD is, I blame it for many of the barriers to generally good physical and mental health that I face,” she told Euronews Health. She also links her severe phobia of vomiting to the condition, as the pressure buildup in her chest sometimes induces nausea.
Despite increasing awareness, R-CPD remains largely unrecognized by healthcare professionals. “There is a treatment for the condition, but it is not NHS-approved yet because many doctors are unaware of it or don’t consider it a health issue,” said Mr. Yakubu Karagama, a laryngologist at Guy’s and St Thomas’ NHS Foundation Trust. He argues that the condition is often dismissed as a social issue rather than a legitimate medical concern.
The Challenges of Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosing R-CPD typically requires an endoscopy, but few doctors specialize in the condition. The most effective treatment currently available is botulinum toxin (Botox) injections into the cricopharyngeus muscle, which helps relax the muscle and allow burping. However, the treatment is costly—upwards of £3,000 (€3,621) through private healthcare in the UK—and is not widely covered by insurance due to the condition’s relatively recent recognition.
A recent study by Texas-based researchers found that individuals with R-CPD were more likely to struggle with anxiety, depression, and social embarrassment, impacting their professional and personal lives. “Sitting up at my desk for full days is actively painful,” Dulcie said. “I can’t do anything in the evenings because I have to lie down for the gurgles and pain to subside.”
For Amelia, a 41-year-old who was formally diagnosed with R-CPD, the condition severely impacted her social life. “I couldn’t drink with my food, couldn’t enjoy nights out or meals out. It was embarrassing, painful, and socially debilitating,” she said. After receiving Botox treatment six years ago at a cost of £5,000 (€6,038), she described it as “the best money I’ve ever spent.”
Alternative Approaches and Hope for the Future
While Botox treatment is effective in about 90% of cases, the procedure carries risks, including temporary acid reflux and swallowing difficulties. Some patients have reported success with alternative methods, such as physical exercises targeting the neck and throat muscles.
Dr. Lee Akst, a laryngologist at Johns Hopkins Medicine, suggests head posture exercises may encourage burping. However, he acknowledges that success rates are anecdotal, with no standardized regimen available.
For now, many individuals suffering from R-CPD continue to push for greater medical recognition and accessibility to treatment. “If this works, it will change my life,” said Dulcie, who is scheduled for treatment soon. “I’ll be able to eat a full meal out with friends without retreating home in discomfort.”
As awareness grows, there is hope that increased research and recognition will lead to broader medical acknowledgment and more affordable treatment options for those living with no-burp syndrome.
Health
Study Finds Weight-Loss Drugs May Protect Heart After Attack
Weight-loss medications commonly prescribed for diabetes and obesity may also help patients recover after a heart attack by improving blood flow and reducing the risk of complications, according to new research.
A study led by scientists at Bristol Medical School found that GLP-1 receptor agonists can help prevent further damage to heart tissue following emergency treatment. The findings were published in the journal Nature Communications.
“In nearly half of all heart attack patients, tiny blood vessels within the heart muscle remain narrowed, even after the main artery is cleared during emergency medical treatment,” said lead author Svetlana Mastitskaya. This condition, known as “no-reflow,” prevents oxygen-rich blood from reaching parts of the heart, increasing the risk of long-term damage.
The research team conducted experiments in rodents and tested their results using cultivated human heart cells. They found that GLP-1 drugs improved blood flow by activating potassium channels and relaxing pericytes, the muscle cells that surround small blood vessels in the heart. When these cells relax, constricted vessels can widen, allowing blood to circulate more effectively.
GLP-1 receptor agonists mimic a hormone produced naturally in the body that helps regulate blood sugar and appetite. They are widely used to treat type 2 diabetes and to promote weight loss by helping patients feel full for longer periods.
Previous studies have shown that people taking GLP-1 medications have a lower risk of cardiovascular diseases, including heart attacks and strokes. In 2024, the US Food and Drug Administration approved the use of Wegovy, a semaglutide-based GLP-1 drug, to reduce the risk of stroke, heart attack and other cardiovascular conditions.
Clinical trials have indicated that the heart benefits of these medications appear to be independent of the amount of weight lost. Patients taking the drugs experienced fewer heart attacks and strokes regardless of whether they were mildly overweight or severely obese.
Researchers believe GLP-1 drugs may lower cardiovascular risk by reducing inflammation, improving blood pressure control, lowering cholesterol and other blood fats, and supporting the health of blood vessels.
Despite these promising findings, experts stress that medication alone is not enough. A recent study from Harvard University found that patients with type 2 diabetes who combined GLP-1 treatment with healthy lifestyle habits saw significantly greater heart health benefits. Those who followed eight key habits, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, adequate sleep and avoiding smoking, had a 60 percent lower risk compared with those who followed one or none.
Frank Hu, one of the study’s authors, said the results show that healthy living remains central to reducing cardiovascular risk, even with modern drug therapies.
Health
Greenland Responds to US Claims, Emphasizes Need for Foreign Healthcare Staff
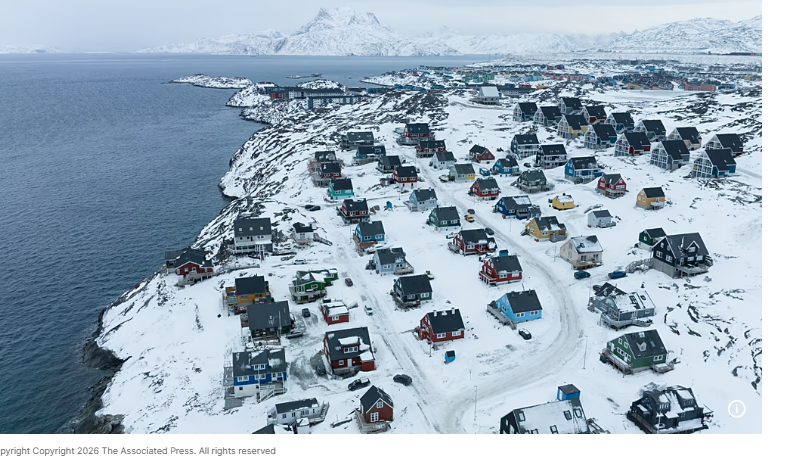

Greenland’s government has highlighted the need to strengthen its health system and recruit foreign healthcare professionals following a statement from US President Donald Trump suggesting patients in the territory are not receiving adequate care. On 22 February, Trump posted on Truth Social that he planned to send a hospital ship to Greenland “to take care of the many people who are sick and not being taken care of there.”
Greenland’s Prime Minister Jens-Frederik Nielsen rejected the offer, stressing that the country provides free healthcare for all residents, a service the United States cannot replicate. Yet Trump’s comments reflect ongoing challenges in staffing Greenland’s healthcare sector.
The territory has long struggled to recruit and retain medical professionals. In response, the government has introduced measures to ease residence permits for foreign healthcare workers. Anna Wangenheim, Minister of Health and Persons with Disabilities, stated on Facebook that Greenland is actively working to strengthen its healthcare system and is seeking more international professionals. She added that help from any country, including the United States, would be welcome if healthcare workers respect local patients, language, and culture.
Greenland, home to more than 56,000 people as of January 2026, is the world’s least densely populated territory. Around 20,000 live in the capital, Nuuk, while the rest reside in scattered towns and settlements, presenting unique logistical challenges for healthcare delivery.
The territory’s health burden remains high. In 2023, Disability-Adjusted Life Years (DALYs) per 100,000 residents stood at 38,715, higher than Denmark’s 30,931 and the European average of 36,863. About 1.5% of the population had cancer and nearly 19% suffered from mental health disorders, both above EU averages. Life expectancy also lags behind Europe, with newborn boys expected to live 69.3 years and girls 73.9 years, compared with the European average of 81.7 years.
Greenland’s health system operates across 70 locations with roughly 120 medical positions—only half of which are permanent—and 300 nursing roles, two-thirds permanent. Services are divided into five regions, each served by a regional hospital, with Queen Ingrid’s Hospital in Nuuk acting as both a regional and national facility. More advanced procedures, such as radiotherapy or invasive cardiology, require travel to Denmark.
Telemedicine has helped bridge geographic gaps. Hansen, a medical advisor at Greenland’s Department of Health, noted that skin diseases can now be diagnosed remotely with support from Denmark. In 2023, the territory launched the app Puisa to provide secure video consultations for residents in remote areas, reducing the need for long travel.
While Greenland’s healthcare system covers basic medical needs, officials acknowledge that infrastructure and staffing limits restrict the delivery of specialized treatments locally. The government continues to seek international staff to enhance services and meet the challenges of a dispersed population.
Health
Eli Lilly’s Oral Pill Shows Strong Weight Loss Results in Clinical Trials

Eli Lilly’s new oral pill, orforglipron, has demonstrated up to 8% weight loss in clinical trials, outperforming existing oral semaglutide alternatives. The results signal growing competition in the weight-loss drug market, where demand for convenient and effective treatments continues to rise.
The trial, published in The Lancet, involved more than 1,600 participants with type 2 diabetes across over 130 research centres in five countries. Participants were assigned to different doses of orforglipron, ranging from 12mg to 36mg, or equivalent doses of oral semaglutide for one year.
Results showed that roughly 60% of those taking orforglipron lost at least 5% of their body weight, compared with 40% of participants on semaglutide. Between 28% and 44% of patients on orforglipron lost 10% or more, while only 13% to 21% of those on semaglutide reached similar reductions. Participants also experienced improved blood sugar control, with orforglipron lowering glucose levels more effectively than its competitor.
Experts welcomed the results but urged caution. Naveed Sattar, professor of cardiometabolic medicine at the University of Glasgow, said oral medications that help patients lose weight and maintain it are vital, noting that excess weight is a key driver of type 2 diabetes and associated cardiovascular risks. Marie Spreckley, a weight management researcher at Cambridge University, highlighted that while the trial showed benefits, side effects and long-term safety remain important considerations.
Adverse effects were more common among orforglipron users. Approximately 9-10% of participants stopped the treatment due to gastrointestinal issues, compared with about 5% of those on semaglutide. Spreckley noted that these effects could affect real-world tolerability outside the trial environment and called for further research on long-term outcomes, including cardiovascular health and sustained effectiveness.
Orforglipron is designed as a daily pill that does not require food or water restrictions, offering a more convenient alternative to injectable treatments such as Ozempic, Wegovy, and Mounjaro. Eli Lilly, which also markets Zepbound and Mounjaro, is positioning orforglipron as a competitor to Novo Nordisk, the current provider of the only approved oral GLP-1 pill.
The pill is under review by the US Food and Drug Administration. If approved, Eli Lilly said US patients with obesity could access the drug starting at $149 (€125.92) for the lowest dose, with higher doses priced up to $399 (€337) if insurance does not cover the cost.
As pharmaceutical companies race to make weight-loss treatments more accessible, orforglipron’s strong results highlight the potential of oral GLP-1 therapies to reshape the market, even as questions about side effects and long-term safety remain.
-

 Entertainment2 years ago
Entertainment2 years agoMeta Acquires Tilda Swinton VR Doc ‘Impulse: Playing With Reality’
-

 Business2 years ago
Business2 years agoSaudi Arabia’s Model for Sustainable Aviation Practices
-

 Business2 years ago
Business2 years agoRecent Developments in Small Business Taxes
-

 Home Improvement1 year ago
Home Improvement1 year agoEffective Drain Cleaning: A Key to a Healthy Plumbing System
-

 Politics2 years ago
Politics2 years agoWho was Ebrahim Raisi and his status in Iranian Politics?
-

 Business2 years ago
Business2 years agoCarrectly: Revolutionizing Car Care in Chicago
-

 Sports2 years ago
Sports2 years agoKeely Hodgkinson Wins Britain’s First Athletics Gold at Paris Olympics in 800m
-

 Business2 years ago
Business2 years agoSaudi Arabia: Foreign Direct Investment Rises by 5.6% in Q1