Health
Countries Eye WHO Exit Despite Legal Uncertainty
Health
Global Recall of Infant Formula by Nestlé, Danone, and Lactalis Over Toxic Contamination

Three of the world’s largest dairy companies, Nestlé, Danone, and Lactalis, have recalled infant formula products worldwide following the detection of cereulide contamination, a toxin that can cause vomiting, diarrhoea, and abdominal cramps.
The contamination has been traced to a single Chinese supplier of ARA (arachidonic acid) oil, a key ingredient in premium infant formulas. Lactalis recently announced the recall of six batches of its Picot brand, which had been distributed across 18 countries. The affected formula has been on sale since January 2025, with expiration dates extending up to March 2027.
“Upon receiving this alert, LNS (Lactalis Nutrition Santé) immediately initiated testing through an accredited independent laboratory to assess the potentially affected products,” the company said in a statement. Lactalis noted that no complaints or reports related to consumption of the products have been received from French authorities so far.
Danone’s recall is smaller, involving only a single batch produced in Thailand. The recall was requested by Singapore’s Food Agency before the batch reached the market. A company spokesperson told Euronews Health that all products undergo rigorous testing and comply with both international and local regulations. “All controls confirm that the products are safe and fully compliant, and no irregularities in relation to Bacillus cereus or Good Manufacturing Practices have been identified,” the spokesperson said.
Nestlé was the first company to withdraw its formula from over 60 countries after detecting contamination at a facility in the Netherlands. The recall, which includes multiple brands such as SMA, Beba, Guigoz, and Alfamino, is one of Nestlé’s largest ever. “Food safety and the wellbeing of all infants remain our top priority,” the company said. “We understand that this news may cause concern, and we are committed to providing clear, transparent information and support for parents and caregivers throughout this process.”
However, consumer groups have questioned Nestlé’s transparency. Foodwatch Netherlands reported that the company confirmed the contamination in early December 2025, but public recalls did not begin until January 2026. Nicole van Gemert, director of foodwatch Netherlands, criticised the delayed communication: “How does Nestlé, which is supposed to ensure immediate traceability of sensitive baby products, explain the piecemeal dissemination of information and late recalls in many countries?”
Despite the recalls, no illnesses have been reported in connection with the affected formula products. Authorities continue to monitor the situation, and parents are advised to check the batch numbers of formulas they have purchased to ensure they are not using contaminated products.
The recalls highlight ongoing challenges in global food safety and supply chains, particularly for infant nutrition products, where contamination can pose significant risks and trigger international concern.
Health
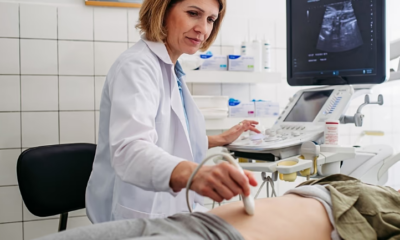
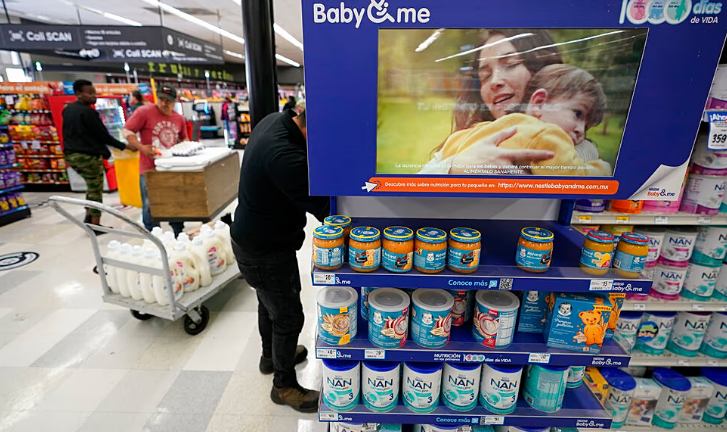
FDA Clears AI Tool to Improve Detection of Fetal Abnormalities in Ultrasounds
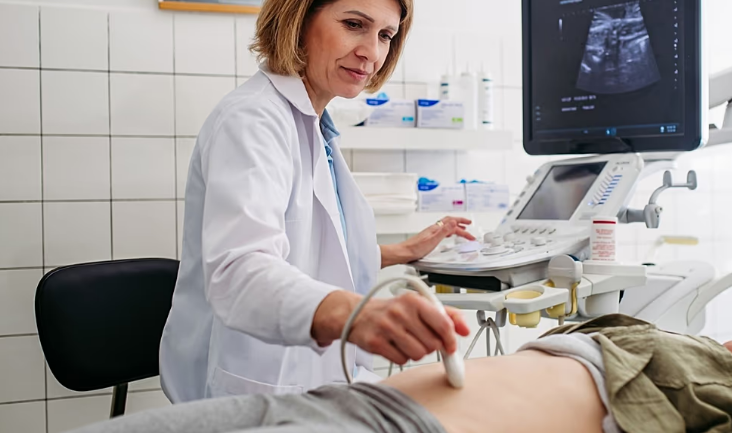
A new artificial intelligence software designed to enhance prenatal ultrasound screenings has received clearance from the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA), offering a potential boost to the detection of fetal abnormalities.
Developed by the American start-up BioticsAI, the tool integrates with existing ultrasound machines to analyze images in real time, highlighting potential issues during scans. Prenatal ultrasounds are widely used throughout pregnancy to identify potential problems in a developing fetus, including malformations in organs or limbs. Yet studies suggest that routine scans can miss a significant number of abnormalities.
According to research, a single early scan performed between 11 and 14 weeks of pregnancy detects only about 38 percent of birth defects. A mid-pregnancy scan, typically conducted between 18 and 24 weeks, identifies roughly 51 percent of abnormalities. When both scans are performed, detection rises to 84 percent, leaving a remaining gap in diagnosis.
BioticsAI’s software works by analyzing each fetal image as it is captured. It evaluates image quality, suggesting adjustments to ensure a clear view of the fetus, and checks whether all parts of the baby are visible. Using data patterns drawn from a global database, the system can detect anomalies, including heart or limb defects, and flag them for the doctor during the scan. After the examination, the software generates a report compiling all findings for clinical review.
Developers say the tool can also save healthcare professionals roughly eight minutes per patient in documentation time. The FDA’s clearance confirms that the software meets medical device performance standards and can be safely integrated into current ultrasound systems.
The approval comes amid ongoing challenges in prenatal care. In Europe, major congenital anomalies occur in about 23.9 per 10,000 births. AI-driven tools are emerging as a promising supplement to conventional scans. French companies Diagnoly and Sonio Detect have also received approval for AI-assisted ultrasound solutions, which automatically identify fetal structures and detect potential heart issues.
Experts say integrating AI into prenatal care could improve early detection rates and help doctors provide timely interventions or monitoring. Real-time feedback during scans ensures that images are complete and abnormalities are less likely to be missed.
BioticsAI’s FDA-cleared tool is expected to be rolled out in clinics across the United States, offering clinicians an additional layer of support in detecting congenital abnormalities. As AI technologies continue to expand in healthcare, prenatal care is emerging as a key area where machine learning can complement human expertise, improving outcomes for both mothers and babies.
Health
Early Flu Wave Hits Europe as Experts Offer Tips to Ease Symptoms

Most people catch a cold in winter, battling fatigue, runny noses, sneezes, coughs, and congestion. This season, an unusually early flu wave has affected millions across Europe, prompting health authorities to offer guidance on managing symptoms.
Typically, influenza season runs from mid-November to late May. However, figures from the European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC) indicate that cases in 2025 surged three to four weeks earlier than in the previous two seasons. The agency reports that flu circulation remains high, though it has recently peaked in most regions.
While there are no specific cures for the flu and the common cold, some simple measures can help manage symptoms and improve comfort. Experts recommend a combination of hydration, rest, and symptom relief to support recovery.
Drinking enough fluids is particularly important. Water, broths, and warm beverages with honey, lemon, or ginger can help prevent dehydration, loosen mucus, and soothe irritated airways. Health authorities caution against alcohol, coffee, and other caffeinated drinks, which can act as diuretics and worsen congestion and sore throats.
Gargling with warm salt water is another simple measure to ease throat pain and reduce inflammation. Mixing one teaspoon of salt in a cup of warm water and using it several times a day can provide relief and help clear mucus.
Rest is essential for recovery. Adults are advised to sleep seven to nine hours a night, and to take naps as needed to allow the immune system to combat the virus. Light exercise such as short walks or yoga may be suitable for mild symptoms, but physical activity should be avoided if fever is present or chest symptoms worsen, to prevent complications.
Maintaining moisture in the environment can also alleviate symptoms. Dry air worsens congestion and sore throats, while humidified air hydrates airways and helps clear mucus. Higher humidity can also reduce how long some respiratory viruses survive in the air.
Medicines can relieve symptoms but do not cure viral infections. Decongestants, such as saline sprays or drops, can ease nasal congestion. Painkillers, including ibuprofen, may reduce fever and discomfort in adults. Antibiotics are not effective against colds or flu and should be avoided to prevent antibiotic resistance.
Health authorities emphasize that these measures, combined with good hygiene and vaccination where appropriate, are key to limiting the impact of seasonal viruses. The ECDC notes that most healthy adults recover from flu within about a week, while a common cold may last up to two weeks.
With the early flu wave affecting millions across Europe, simple steps such as staying hydrated, resting, and taking appropriate symptom relief can help patients recover safely and reduce strain on healthcare services.
-

 Entertainment1 year ago
Entertainment1 year agoMeta Acquires Tilda Swinton VR Doc ‘Impulse: Playing With Reality’
-

 Business2 years ago
Business2 years agoSaudi Arabia’s Model for Sustainable Aviation Practices
-

 Business2 years ago
Business2 years agoRecent Developments in Small Business Taxes
-

 Home Improvement1 year ago
Home Improvement1 year agoEffective Drain Cleaning: A Key to a Healthy Plumbing System
-

 Politics2 years ago
Politics2 years agoWho was Ebrahim Raisi and his status in Iranian Politics?
-

 Business2 years ago
Business2 years agoCarrectly: Revolutionizing Car Care in Chicago
-

 Sports1 year ago
Sports1 year agoKeely Hodgkinson Wins Britain’s First Athletics Gold at Paris Olympics in 800m
-

 Business2 years ago
Business2 years agoSaudi Arabia: Foreign Direct Investment Rises by 5.6% in Q1