Health
UK Ranks Lowest in Children’s Well-Being in Europe Amid Growing Concerns Over Life Satisfaction
Health
Greenland Responds to US Claims, Emphasizes Need for Foreign Healthcare Staff
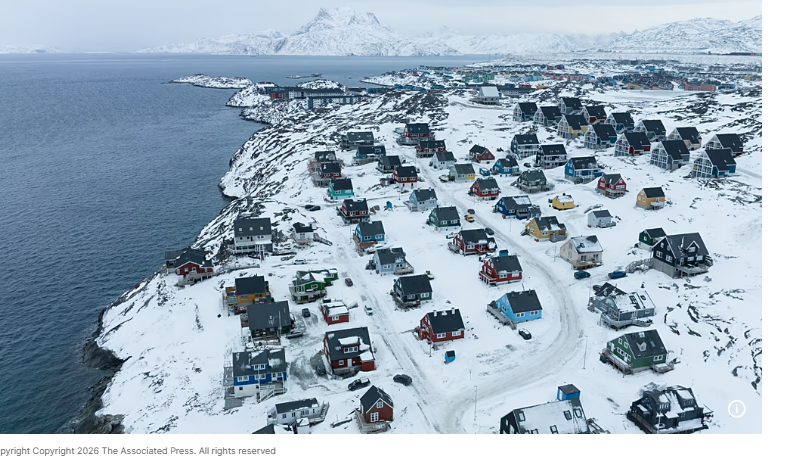

Greenland’s government has highlighted the need to strengthen its health system and recruit foreign healthcare professionals following a statement from US President Donald Trump suggesting patients in the territory are not receiving adequate care. On 22 February, Trump posted on Truth Social that he planned to send a hospital ship to Greenland “to take care of the many people who are sick and not being taken care of there.”
Greenland’s Prime Minister Jens-Frederik Nielsen rejected the offer, stressing that the country provides free healthcare for all residents, a service the United States cannot replicate. Yet Trump’s comments reflect ongoing challenges in staffing Greenland’s healthcare sector.
The territory has long struggled to recruit and retain medical professionals. In response, the government has introduced measures to ease residence permits for foreign healthcare workers. Anna Wangenheim, Minister of Health and Persons with Disabilities, stated on Facebook that Greenland is actively working to strengthen its healthcare system and is seeking more international professionals. She added that help from any country, including the United States, would be welcome if healthcare workers respect local patients, language, and culture.
Greenland, home to more than 56,000 people as of January 2026, is the world’s least densely populated territory. Around 20,000 live in the capital, Nuuk, while the rest reside in scattered towns and settlements, presenting unique logistical challenges for healthcare delivery.
The territory’s health burden remains high. In 2023, Disability-Adjusted Life Years (DALYs) per 100,000 residents stood at 38,715, higher than Denmark’s 30,931 and the European average of 36,863. About 1.5% of the population had cancer and nearly 19% suffered from mental health disorders, both above EU averages. Life expectancy also lags behind Europe, with newborn boys expected to live 69.3 years and girls 73.9 years, compared with the European average of 81.7 years.
Greenland’s health system operates across 70 locations with roughly 120 medical positions—only half of which are permanent—and 300 nursing roles, two-thirds permanent. Services are divided into five regions, each served by a regional hospital, with Queen Ingrid’s Hospital in Nuuk acting as both a regional and national facility. More advanced procedures, such as radiotherapy or invasive cardiology, require travel to Denmark.
Telemedicine has helped bridge geographic gaps. Hansen, a medical advisor at Greenland’s Department of Health, noted that skin diseases can now be diagnosed remotely with support from Denmark. In 2023, the territory launched the app Puisa to provide secure video consultations for residents in remote areas, reducing the need for long travel.
While Greenland’s healthcare system covers basic medical needs, officials acknowledge that infrastructure and staffing limits restrict the delivery of specialized treatments locally. The government continues to seek international staff to enhance services and meet the challenges of a dispersed population.
Health
Eli Lilly’s Oral Pill Shows Strong Weight Loss Results in Clinical Trials

Eli Lilly’s new oral pill, orforglipron, has demonstrated up to 8% weight loss in clinical trials, outperforming existing oral semaglutide alternatives. The results signal growing competition in the weight-loss drug market, where demand for convenient and effective treatments continues to rise.
The trial, published in The Lancet, involved more than 1,600 participants with type 2 diabetes across over 130 research centres in five countries. Participants were assigned to different doses of orforglipron, ranging from 12mg to 36mg, or equivalent doses of oral semaglutide for one year.
Results showed that roughly 60% of those taking orforglipron lost at least 5% of their body weight, compared with 40% of participants on semaglutide. Between 28% and 44% of patients on orforglipron lost 10% or more, while only 13% to 21% of those on semaglutide reached similar reductions. Participants also experienced improved blood sugar control, with orforglipron lowering glucose levels more effectively than its competitor.
Experts welcomed the results but urged caution. Naveed Sattar, professor of cardiometabolic medicine at the University of Glasgow, said oral medications that help patients lose weight and maintain it are vital, noting that excess weight is a key driver of type 2 diabetes and associated cardiovascular risks. Marie Spreckley, a weight management researcher at Cambridge University, highlighted that while the trial showed benefits, side effects and long-term safety remain important considerations.
Adverse effects were more common among orforglipron users. Approximately 9-10% of participants stopped the treatment due to gastrointestinal issues, compared with about 5% of those on semaglutide. Spreckley noted that these effects could affect real-world tolerability outside the trial environment and called for further research on long-term outcomes, including cardiovascular health and sustained effectiveness.
Orforglipron is designed as a daily pill that does not require food or water restrictions, offering a more convenient alternative to injectable treatments such as Ozempic, Wegovy, and Mounjaro. Eli Lilly, which also markets Zepbound and Mounjaro, is positioning orforglipron as a competitor to Novo Nordisk, the current provider of the only approved oral GLP-1 pill.
The pill is under review by the US Food and Drug Administration. If approved, Eli Lilly said US patients with obesity could access the drug starting at $149 (€125.92) for the lowest dose, with higher doses priced up to $399 (€337) if insurance does not cover the cost.
As pharmaceutical companies race to make weight-loss treatments more accessible, orforglipron’s strong results highlight the potential of oral GLP-1 therapies to reshape the market, even as questions about side effects and long-term safety remain.
Health
Vasectomy Gains Popularity Among Polish Men as Fertility Rates Fall
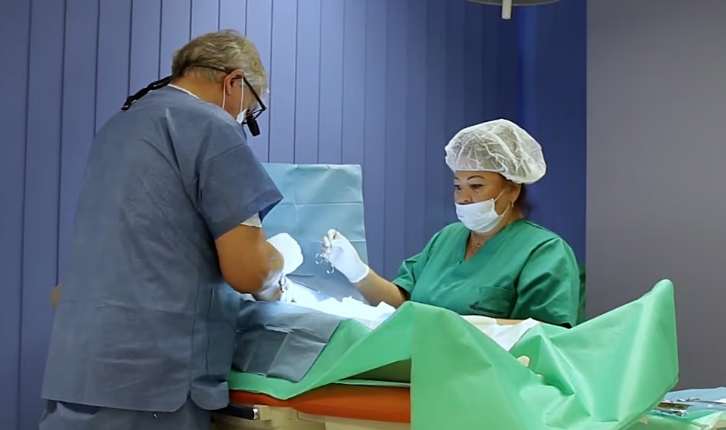
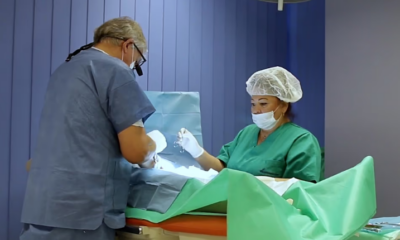
In Poland, vasectomy is emerging as a more popular method of permanent contraception among men, while female tubal ligation remains illegal on request. The trend comes amid growing concern over the country’s declining fertility rates and shifting attitudes toward family planning.
The State of the Young 2025 report found that 15 percent of adults born between 1995 and 2006 have no children and do not intend to have any. While permanent contraception options for men are increasingly sought, women in Poland have no equivalent choice: tubal ligation is prohibited except for strict medical reasons, and performing it on request can carry prison sentences of three to 20 years under Article 156-1 of the Penal Code.
Statistics on vasectomy in Poland are limited, as most procedures are carried out privately. It is estimated that around 5,000 vasectomies take place annually, with clinics advertising the services online and on roadside billboards. Mateusz Siwik, owner of a Warsaw clinic, told Euronews Health that interest in the procedure has been steadily growing, with year-on-year increases of around 15 percent. He said patients are socially diverse but often men in stable relationships with two or more children who have consciously decided to end family expansion.
One example is Kamil Pawelski, a psychologist and influencer who underwent vasectomy in 2020 after the birth of his second child. Pawelski said the decision was motivated by concern for his wife’s health and their mutual decision not to have more children. He noted that public reactions were mixed, with more criticism coming from men than women. “I think this is a very masculine decision,” he said, stressing that the procedure is only suitable for those certain about not having future children.
The restriction on female sterilisation has contributed to medical tourism, with Poles travelling to Germany, Czechia, and Slovakia for tubal ligation. Rafał Zadykowicz, an obstetrics and gynaecology specialist, said foreign gynaecologists are often surprised by the strict legal limits in Poland, where access is limited to medical necessity.
Vasectomy is increasingly preferred across Europe and North America due to its relative simplicity and low invasiveness. France has seen vasectomies rise from 1,940 in 2010 to over 30,000 in 2022, especially among men under 40. In Canada, 22 percent of women rely on their partner’s vasectomy, while rates in the UK, New Zealand, and South Korea range from 17 to 21 percent. In contrast, Italy sees only around 1 percent of men undergoing the procedure. No official figures exist for Poland, but interest is clearly rising.
Poland faces some of the lowest fertility rates globally. The total fertility rate fell to an estimated 1.10 children per woman in 2025, leaving the population at 37.3 million. Within the OECD, Poland ranks third from last, ahead of only Chile and South Korea. Social policy programmes offering financial support for children have been in place since 2016, but debates continue over why many young adults choose not to have children despite the incentives.
-

 Entertainment2 years ago
Entertainment2 years agoMeta Acquires Tilda Swinton VR Doc ‘Impulse: Playing With Reality’
-

 Business2 years ago
Business2 years agoSaudi Arabia’s Model for Sustainable Aviation Practices
-

 Business2 years ago
Business2 years agoRecent Developments in Small Business Taxes
-

 Home Improvement1 year ago
Home Improvement1 year agoEffective Drain Cleaning: A Key to a Healthy Plumbing System
-

 Politics2 years ago
Politics2 years agoWho was Ebrahim Raisi and his status in Iranian Politics?
-

 Business2 years ago
Business2 years agoCarrectly: Revolutionizing Car Care in Chicago
-

 Sports2 years ago
Sports2 years agoKeely Hodgkinson Wins Britain’s First Athletics Gold at Paris Olympics in 800m
-

 Business2 years ago
Business2 years agoSaudi Arabia: Foreign Direct Investment Rises by 5.6% in Q1