Business
Eurozone Retail Trade Stagnates as Economic Challenges Persist
Retailers in the eurozone ended 2024 on a subdued note, with data signaling limited growth and a challenging outlook for 2025. According to Eurostat figures released Thursday, the seasonally adjusted volume of retail trade in the euro area rose by a mere 0.1% in November compared to October.
The modest uptick followed declines of 0.3% in October and a 0.5% gain in September, underscoring the sector’s struggles. Across the European Union, retail trade fared slightly better with a 0.2% increase in November, after a 0.1% dip in October and a 0.4% rise in September.
Despite these figures, retail sales remain well below their November 2021 peak and the pre-pandemic trend, said Andrew Kenningham, chief Europe economist at Capital Economics. He characterized the post-pandemic recovery as “disappointing,” attributing sluggish growth to lingering effects of COVID-19 disruptions and the war in Ukraine.
The eurozone grappled with an inflationary peak in 2022, driven by supply chain disruptions and energy price shocks. Although inflation has eased and the European Central Bank (ECB) has embarked on a rate-cutting trajectory, tighter fiscal conditions continue to weigh on consumer spending.
Key Trends in November
November’s modest growth was supported by a 0.8% rise in automotive fuel trade and a 0.1% increase in food, drink, and tobacco sales. However, sales of non-food products (excluding fuel) declined by 0.6%, highlighting uneven performance across sectors.
Among member states, Cyprus recorded the strongest monthly retail trade growth at 2.3%, followed by Bulgaria (1.3%), and Denmark and Latvia (both 1.1%). Conversely, Belgium experienced the steepest decline at -2.4%, with Germany and Spain both reporting -0.6%, and Poland and Finland recording -0.2%. France saw a modest 0.3% rise.
Challenges and Outlook for 2025
Looking ahead, economists predict a modest recovery rather than a robust rebound in retail trade. Rising real incomes, moderate employment growth, and falling interest rates are expected to provide some support for consumption. However, the pace of real income growth is projected to slow in 2025, dampening prospects for a strong recovery.
“November’s weaker retail sales are more due to less willingness to spend than a lack of purchasing power,” said Peter Vanden Houte, chief economist at ING Belgium. He attributed the cautious consumer behavior to fears of higher unemployment and geopolitical uncertainties.
The outlook remains clouded by political challenges in France and Germany, as well as potential policy shifts under the new U.S. administration. Economists agree that meaningful acceleration in retail trade is unlikely before the second half of 2025, as restructuring and layoffs in European manufacturing continue to weigh on confidence.
For now, eurozone retailers face a slow path to recovery, with significant headwinds still in play.
Business
Oil Tanker Attacked in Strait of Hormuz, Crew Evacuated
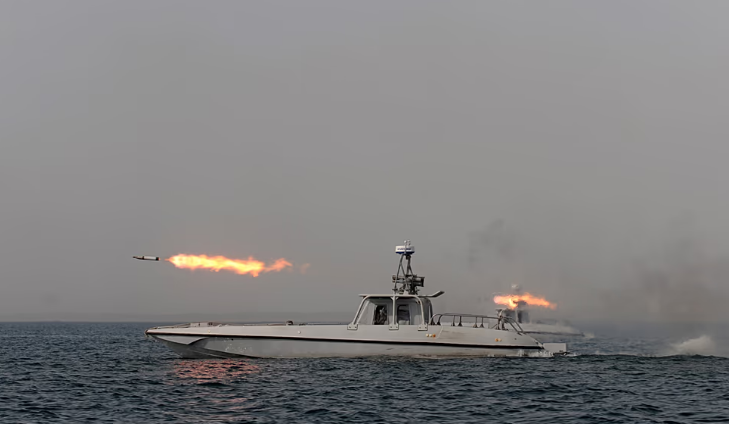

An oil tanker was attacked off the coast of Musandam in the Strait of Hormuz on Sunday, leaving four people injured and prompting the evacuation of all 20 crew members, according to Oman’s Maritime Security Centre.
The vessel, named Skylight and flying the flag of the Republic of Palau, was targeted around five nautical miles (9.26 km) north of Khasab Port, Oman authorities said. The incident marked the first reported attack on a ship in the strategic Strait of Hormuz on Sunday morning.
Oman’s Maritime Security Centre confirmed that the tanker’s crew included 15 Indian nationals and five Iranian nationals, all of whom were safely evacuated. The four injured crew members were transferred for medical treatment. Authorities did not immediately provide details on the cause of the attack or the identities of the attackers.
The incident has heightened concerns about shipping safety in one of the world’s most important oil transit routes. The Strait of Hormuz handles a significant portion of global crude oil exports, and any disruption to its operations can have major implications for energy markets.
In response to the attack, major shipping companies have suspended operations through the Strait of Hormuz. Danish shipping and logistics giant Maersk announced on Sunday afternoon that it had halted all future transits through the waterway until further notice. Other operators are reportedly reviewing their shipping schedules and implementing additional safety measures.
The attack comes amid ongoing regional tensions, with the Strait of Hormuz often at the center of geopolitical disputes. Analysts say the incident could lead to further disruptions in global oil supplies and push energy prices higher if shipping companies continue to avoid the area.
Maritime security experts emphasize the need for close monitoring of shipping traffic and coordinated responses to ensure the safety of vessels and crews in the region. The rapid evacuation of Skylight’s crew has been described as a positive example of emergency preparedness, but the attack underscores the continuing risks faced by commercial shipping in the Gulf.
Authorities are continuing to investigate the circumstances of the attack and are coordinating with international maritime agencies to prevent further incidents. The situation remains fluid, and the potential impact on shipping and regional security is likely to unfold in the coming days.
Business
EU Household Energy Prices Remain Above Pre-War Levels Despite Stabilisation

Residential electricity and natural gas prices across the European Union remain higher than before Russia’s invasion of Ukraine, even though markets have steadied in recent years.
The war, which began in February 2022 and has now entered its fifth year, reshaped Europe’s energy landscape. According to the European Council, Russia’s share of EU pipeline gas imports fell sharply from around 40 per cent in 2021 to about 6 per cent in 2025, following sanctions, embargoes and efforts to diversify supplies.
New data from Eurostat show that between the first half of 2021 and the first half of 2025, household electricity prices in the EU rose 30 per cent, from 22 cents per kilowatt-hour to 28.7 cents. Over the same period, natural gas prices climbed 79 per cent, from 6.4 cents to 11.4 cents per kilowatt-hour.
The Household Energy Price Index (HEPI), compiled by Energie-Control Austria, MEKH and VaasaETT, tracks monthly end-user prices in European capital cities. Its January 2026 figures indicate that electricity prices across EU capitals were 5 per cent higher than in January 2022. However, compared with January 2021, prices were up 38 per cent.
Some cities experienced particularly sharp increases over the five-year period. Electricity prices more than doubled in Vilnius, rising 102 per cent. Other large jumps were recorded in Bucharest (88 per cent), Bern (86 per cent), Kyiv (77 per cent), Amsterdam (75 per cent), Riga (74 per cent), Brussels (67 per cent) and London (64 per cent).
Only Copenhagen and Budapest posted declines over that period, at minus 16 per cent and minus 8 per cent respectively.
Among the capitals of Europe’s five largest economies, London and Rome saw notable increases, while Madrid and Berlin recorded relatively modest rises. Paris remained below the EU average increase.
Energy analysts at the European Energy and Climate Policy (IEECP) say the electricity mix has been a decisive factor. Countries such as Spain benefit from a higher share of wind, solar and hydropower, while Nordic nations rely heavily on hydropower, geothermal and wind energy, reducing exposure to fossil fuel price swings.
Looking only at the period from January 2022 to January 2026 presents a different trend. Copenhagen recorded a 44 per cent fall in electricity prices, while London, Madrid, Berlin and Rome also saw declines. Paris, by contrast, registered a 21 per cent increase. Vilnius showed the largest EU rise at 70 per cent, while Kyiv topped the overall list at 87 per cent.
Natural gas prices across EU capitals edged down by 1 per cent between January 2022 and January 2026. Berlin, Brussels and Athens recorded declines of around 40 per cent, while Riga, Warsaw and Lisbon saw strong increases.
Despite the recent stabilisation, household energy bills across much of Europe remain well above pre-invasion levels, reflecting the lasting impact of the energy crisis.
Business
Transatlantic Tensions on Digital Rules Highlight Need for Cooperation

Discussions between Europe and the United States over digital regulation continue to be marked by miscommunication and frustration, even as competitors observe from the sidelines. Europeans and Americans talk past each other while rivals watch. The European Union can set its own standards, but in an interconnected economy, decoupling fantasies and grandstanding won’t help.
The debate often centres on “free speech” concerns voiced by U.S. tech companies and policymakers in response to the EU’s legislative framework for digital platforms. In Europe, such narratives typically prompt defensive reactions. Some Europeans respond with a blunt message: “This is our land, our Union, our laws, follow them, or leave the EU—we’ll find alternative products to use!” Public awareness of American constitutional amendments is low across Europe, just as Americans pay little attention to European digital acts and regulations.
The transatlantic dialogue is further complicated by the global nature of social media platforms. Any EU legislation affecting user experience inevitably influences the functioning of these platforms worldwide, touching on what Americans see as free speech rights. The EU also seeks to extend its influence through the “Brussels effect,” ensuring that European rules shape global standards, while the U.S. maintains a large trade surplus in services and competes technologically with China. This mix of economic, political, and regulatory factors explains why U.S. attention is sharply focused on Europe’s digital policies.
Europeans argue that their 450-million-consumer market has the right to set rules that reflect local principles and values. Attempts to adjust or simplify regulations are difficult, with efforts often met with political resistance and scrutiny. The regulatory ecosystem in Europe supports industries of lawyers, consultants, and experts whose work depends on maintaining complex rules, making reform a sensitive topic.
On the American side, anti-EU rhetoric by public figures has sometimes compounded the problem, drowning out moderates and reinforcing defensive European responses. Analysts note that both regions have seen productive voices sidelined as grandstanding and negative statements dominate public discourse.
Observers argue that long-term thinking is necessary. By evaluating the EU-U.S. tech partnership in the broader context of global alliances, including China and Russia, policymakers can better assess priorities and avoid unnecessary disruption. Blank-slate decoupling between Europe and the United States is unrealistic, and delaying constructive dialogue risks broader economic consequences.
Experts warn that continued transatlantic infighting benefits other global powers and weakens the ability of both regions to set coherent standards in emerging technologies. The message from analysts is clear: cooperation, not confrontation, will determine whether the EU and U.S. can maintain leadership in digital regulation while safeguarding economic and technological interests.
-

 Entertainment2 years ago
Entertainment2 years agoMeta Acquires Tilda Swinton VR Doc ‘Impulse: Playing With Reality’
-

 Business2 years ago
Business2 years agoSaudi Arabia’s Model for Sustainable Aviation Practices
-

 Business2 years ago
Business2 years agoRecent Developments in Small Business Taxes
-

 Home Improvement1 year ago
Home Improvement1 year agoEffective Drain Cleaning: A Key to a Healthy Plumbing System
-

 Politics2 years ago
Politics2 years agoWho was Ebrahim Raisi and his status in Iranian Politics?
-

 Business2 years ago
Business2 years agoCarrectly: Revolutionizing Car Care in Chicago
-

 Sports2 years ago
Sports2 years agoKeely Hodgkinson Wins Britain’s First Athletics Gold at Paris Olympics in 800m
-

 Business2 years ago
Business2 years agoSaudi Arabia: Foreign Direct Investment Rises by 5.6% in Q1