Travel
Travel Industry Faces Scrutiny Over Website Accessibility Failures
Travel
Middle East Authorities Warn Against Sharing Footage of Iranian Strikes on Social Media
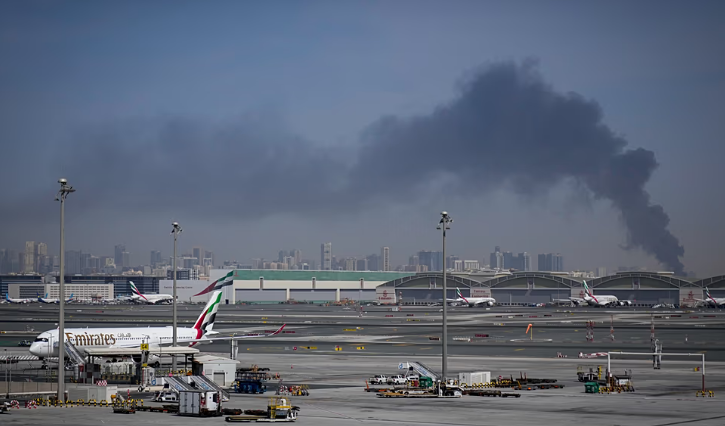

Authorities across the Middle East are cautioning residents, citizens, and visitors about sharing images and videos of Iranian retaliatory strikes, citing security risks and potential legal consequences.
Authorities have restrictions around sharing such images for security purposes and to prevent the spread of fake news. Social media has been flooded with footage from influencers and tourists showing missile interceptions and other military responses in the region. Officials warn that posting such content could reveal the locations of defensive installations or provide information that may aid future attacks.
The concerns are not unique to the region. Similar rules are in place in Ukraine, where the ongoing conflict with Russia has prompted authorities to limit the circulation of footage from conflict zones.
In Bahrain, two people were arrested on February 28 for posting live footage of strikes on social media. The Ministry of Interior said anyone filming, posting, or reposting videos from the scene could face legal action. “This constitutes a legal violation that could harm security and public order,” the ministry stated on X.
Kuwait’s Ministry of Interior issued comparable guidance, asking citizens to refrain from filming missile interceptions or authorities carrying out their duties. The ministry said such content could cause public anxiety, disrupt security operations, and spread inaccurate information. Legal measures will be taken against anyone sharing rumours or misleading news.
Qatar’s Ministry of Interior emphasized avoiding the circulation of images or videos of the aftermath to prevent legal liability. The Dubai Media Office issued similar advice, urging residents to rely on official sources for updates.
Authorities stress the importance of following verified channels for information. Bahrainis can access updates through @moi_bahrain and @bna_en, while UAE residents should refer to @DXBMediaOffice and @ADMediaOffice. Qataris are advised to follow @QNAEnglish and @MOI_QatarEn, and Kuwaitis can check @kuna_en and @Moi_kuw. Jordan and Saudi Arabia have also set up official accounts for timely updates, including @PetranewsEN, @moi_jor, @Spa_Eng, and @MOISaudiArabia.
Several embassies are providing updates to their citizens who register with them. International news outlets such as Euronews are also offering live coverage, with bureaus in Doha and Dubai running continuous updates on their website.
Officials emphasize that following these guidelines protects public safety and ensures accurate reporting during a period of heightened regional tension. Authorities warn that disregarding the rules could carry serious legal consequences, highlighting the need for vigilance and restraint when sharing information online.
Travel
Ryanair Ranks Last in Which? Airline Satisfaction Survey as Jet2 and Singapore Airlines Lead
Travel
AirAsia X to Relaunch London-Kuala Lumpur Route With Bahrain Stopover

AirAsia X’s revived route between London Gatwick and the Malaysian capital will now include a stopover in Bahrain, the airline confirmed. The low-cost long-haul carrier is set to resume flights between London and Kuala Lumpur this summer, offering travellers a new connection via the Middle Eastern hub.
From 26 June 2026, passengers will be able to fly between Gatwick and Kuala Lumpur International Airport with a layover in Bahrain. Stopover times will range from 90 minutes to two hours, bringing the total journey to approximately 16 and a half hours.
The airline has announced promotional fares booked before 22 February for travel between 26 June and 30 November starting at €85 one-way. However, current ticket searches show the lowest available fares for this period at around €185 one-way from London to Kuala Lumpur.
AirAsia X has been steadily expanding its long-haul network. In mid-November, the airline introduced a direct service between Istanbul’s Sabiha Gökçen International Airport and Kuala Lumpur, a flight taking roughly 10 and a half hours.
The London route marks a return to Europe after more than a decade. AirAsia X previously operated direct flights from London and Paris Orly to Kuala Lumpur, but these were discontinued in 2012 due to rising jet fuel prices, higher taxes, and declining demand. Since then, the airline’s leadership, including CEO Tony Fernandes, expressed interest in restoring European services, with plans gradually materialising over the past few years.
Fernandes, now CEO of Capital A, AirAsia’s parent company, described Bahrain as a “strategic hub” for the airline’s European operations. “This is a defining step in the next phase of AAX’s growth,” he said. “Bahrain as our strategic aviation hub allows us to connect Asia with the Middle East and Europe more effectively while creating a scalable platform for future growth. Looking ahead, we will deepen partnerships with airports, tourism authorities and industry stakeholders to unlock new demand corridors.”
The airline has not disclosed which additional European destinations it may target next. Currently, AirAsia X serves around 150 destinations, covering cities in Australia, China, India, Japan, South Korea, and Uzbekistan, reflecting its wide-reaching network across Asia and beyond.
The relaunch of the London-Kuala Lumpur route with a Bahrain stopover signals AirAsia X’s renewed commitment to long-haul operations in Europe, combining affordability with strategic connectivity. For travellers seeking low-cost options on intercontinental flights, the route offers a competitive alternative to traditional carriers, while providing access to the growing Gulf aviation hub.
-

 Entertainment2 years ago
Entertainment2 years agoMeta Acquires Tilda Swinton VR Doc ‘Impulse: Playing With Reality’
-

 Business2 years ago
Business2 years agoSaudi Arabia’s Model for Sustainable Aviation Practices
-

 Business2 years ago
Business2 years agoRecent Developments in Small Business Taxes
-

 Home Improvement1 year ago
Home Improvement1 year agoEffective Drain Cleaning: A Key to a Healthy Plumbing System
-

 Politics2 years ago
Politics2 years agoWho was Ebrahim Raisi and his status in Iranian Politics?
-

 Business2 years ago
Business2 years agoCarrectly: Revolutionizing Car Care in Chicago
-

 Sports2 years ago
Sports2 years agoKeely Hodgkinson Wins Britain’s First Athletics Gold at Paris Olympics in 800m
-

 Business2 years ago
Business2 years agoSaudi Arabia: Foreign Direct Investment Rises by 5.6% in Q1