Technology
TikTok Users Brace for Possible US Ban, Seek Alternatives as Deadline Looms
With TikTok facing a likely ban in the United States within three days, users across the country are preemptively bidding farewell to the platform and exploring alternatives. The uncertainty has sparked a surge in downloads of both new and existing short-form video apps, as users, including influencers, prepare for the potential shutdown.
Influencer Jasmine Chiswell, who boasts 18 million TikTok followers, posted a video on Tuesday lamenting the app’s impending ban. “Me saying goodbye to 18 million best friends because TikTok is getting banned,” read her caption, accompanied by sad emojis.
Countdown to Ban Sparks Anxiety
The fear intensified after The Information reported late Tuesday that TikTok may shut down entirely for U.S. users by Sunday unless it secures a Supreme Court reprieve or finds an American owner. Earlier, many assumed the app would simply be removed from app stores, allowing current users temporary access.
The looming ban stems from U.S. national security concerns over TikTok’s China-based parent company, ByteDance, and the potential sharing of American user data with Beijing.
Rise of TikTok Alternatives
Amid the uncertainty, several lesser-known platforms have gained traction. Apps like RedNote (known as Xiaohongshu), Lemon8, Clapper, Flip, and Fanbase have seen significant downloads in recent days.
RedNote, a China-based app similar to Instagram, has climbed to the top of app store charts. Many U.S. users joined RedNote as a form of protest against the government’s actions. “Take away TikTok, and we’ll just use another Chinese app,” declared one user in a video. The influx of American users on RedNote has sparked humorous cultural exchanges, with users offering Mandarin lessons and sharing slang.
Lemon8, another ByteDance-owned platform, has also gained popularity. Previously marketed to U.S. users in early 2023, Lemon8 offers a Pinterest-like interface with lifestyle content. However, like TikTok, these apps could also face future restrictions under U.S. laws targeting platforms owned by “foreign adversaries.”
Non-Chinese platforms, such as Clapper and Flip, are also gaining momentum. Clapper, which includes live audio conversations, reported 1.4 million new users this week. Flip, a shopping-focused app, experienced such rapid growth that it faced temporary outages.
Mainstream Platforms Struggle to Match TikTok’s Appeal
While mainstream platforms like Instagram Reels and YouTube Shorts stand to benefit, many users argue they lack TikTok’s magic. TikTok’s algorithm, which uniquely predicts users’ preferences, remains unmatched. Creators have expressed concerns about losing TikTok’s authentic community and monetization tools, such as TikTok Shop.
“TikTok favors realism,” said creator Stormi Steele. “It’s about being authentic, and people resonate with that.”
As TikTok’s fate hangs in the balance, its users continue to search for a platform that replicates its unmatched features and community spirit.
Technology
Amazon Begins Test Flights for UK Drone Delivery Service
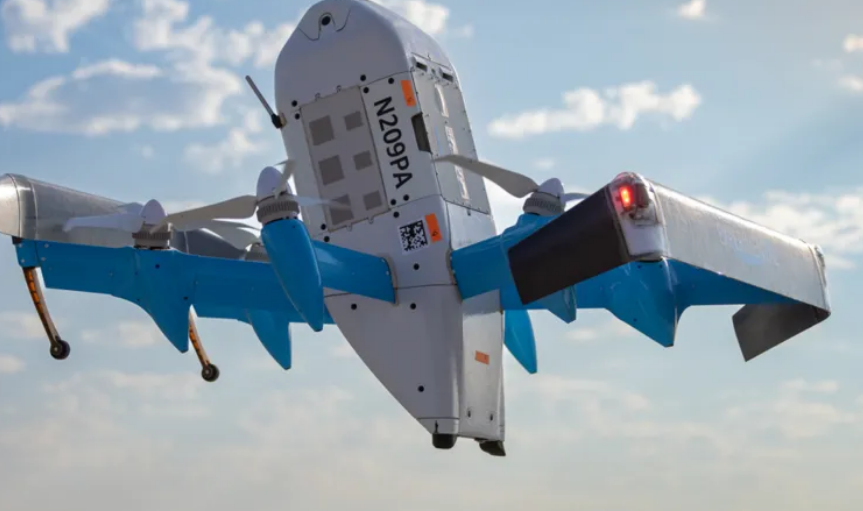

Amazon has started test flights for its UK drone delivery service, marking a key step ahead of the planned launch later this year. The company confirmed that a limited number of drones have taken off from its base in Darlington’s Symmetry Park, although deliveries to customers have not yet begun.
Darlington was chosen last January as Amazon’s UK test centre, and the company plans to use the location to trial airborne deliveries for eligible residents. When the service goes live, packages weighing less than five pounds (2.3 kilograms) will be delivered within two hours, the firm said.
Amazon’s latest drone, the MK30, will be used in the trials. The company highlighted the technology onboard, which allows drones to detect and avoid obstacles such as clotheslines, trampolines, and other hazards that may not appear on satellite maps. Cameras continuously monitor the surrounding airspace and can direct the drone to take evasive action if other aircraft enter its flight path.
“The perception technology relies on sophisticated machine learning models trained to recognise various objects, including people, animals, physical barriers, and other airborne vehicles,” Amazon said.
Safety remains a central focus for the company. David Carbon, vice president of Amazon Prime Air, said the drones are designed to operate quietly and efficiently while prioritising the safety of people, pets, and property. He added that the company is working closely with Darlington Council and the UK Civil Aviation Authority during the testing phase.
“This marks an exciting next step in bringing drone delivery to the UK,” Carbon said. “We look forward to demonstrating how this innovative technology can serve the people of Darlington while maintaining the highest safety standards.”
Amazon’s drone delivery initiative is part of its wider Prime Air programme, which has been in development for several years. The service aims to offer faster delivery times for lightweight packages, using autonomous aircraft that can navigate urban and suburban environments.
The launch in the UK follows successful trials in the United States, where Amazon has been testing similar technology to improve delivery speed and efficiency. As regulations for commercial drone flights evolve, the company is aiming to integrate these autonomous devices into its logistics network while ensuring public safety.
Residents in Darlington may be among the first in the UK to receive packages by air, as Amazon moves closer to making drone deliveries a reality. The company has emphasised that testing will continue carefully, with human oversight and advanced safety systems in place to ensure smooth operations.
Innovation
Open-Source Recycling Movement Gains Ground as Precious Plastic Community Recycles 1,400 Tonnes in One Year
Technology
Calls for European Supergrid Intensify Amid Energy Crises and Climate Pressures

As Europe battles growing climate extremes, energy instability, and geopolitical pressures, momentum is building around a decades-old concept: the European supergrid. The idea, once considered aspirational, is regaining urgency amid widespread power outages and rising reliance on renewable energy.
The European Union is set to install 89 gigawatts of new renewable energy capacity in 2025, a 10-gigawatt increase from the previous year, most of it driven by solar projects. This expansion is central to the EU’s 2030 climate targets, which aim to cut net greenhouse gas emissions by at least 55 percent from 1990 levels. Yet as renewable penetration grows, so too does the need for a more integrated, resilient power network.
Recent blackouts in Spain and Portugal highlighted vulnerabilities in the continent’s energy systems, prompting experts to revisit the supergrid concept. A pan-European high-voltage grid could allow electricity generated from wind in the north or solar in the south to flow seamlessly across borders, balancing supply and demand.
“A supergrid would allow green energy to flow across borders efficiently, balancing supply and demand; it could smooth out energy highs and lows, cut prices, boost resilience, and help Europe ditch fossil fuels faster,” said Michael Ashley Schulman, CIO at Running Point Capital Advisors.
France, Germany, the UK, and Italy are already developing “mini-supergrids” — multi-terminal high-voltage DC (HVDC) networks. Over time, these could be linked like a motorway system, gradually forming a broader supergrid. Offshore grids are also gaining traction as a cost- and carbon-efficient way to integrate large-scale wind energy.
But building a Europe-wide grid is no simple task. Regulatory fragmentation, complex permitting across countries, and local opposition have slowed progress. “Stitching together dozens of national grids isn’t just an engineering project; it’s a political minefield,” Schulman noted.
Beyond logistics, some warn that the supergrid must reflect more than economic efficiency. “A supergrid must serve ecological integrity, social equity, and energy democracy — not just corporate interests,” said Therese Guttmann of Vienna’s Institute for Ecological Economics.
Critics argue that decentralised solutions and local energy systems should develop in parallel to avoid replacing one form of centralisation with another. Others caution against cybersecurity risks and systemic fragility, warning that overconnectivity could make the entire continent vulnerable to disruptions.
The European Commission estimates that €584 billion in grid investment is needed by 2030 to meet energy transition targets. While the supergrid could play a major role, analysts agree it must be part of a broader mix of infrastructure improvements and decentralised technologies.
As the continent continues to navigate a fragile energy landscape, the supergrid remains both a tantalising vision — and a test of Europe’s ability to act collectively.
-

 Entertainment1 year ago
Entertainment1 year agoMeta Acquires Tilda Swinton VR Doc ‘Impulse: Playing With Reality’
-

 Business2 years ago
Business2 years agoSaudi Arabia’s Model for Sustainable Aviation Practices
-

 Business2 years ago
Business2 years agoRecent Developments in Small Business Taxes
-

 Home Improvement1 year ago
Home Improvement1 year agoEffective Drain Cleaning: A Key to a Healthy Plumbing System
-

 Politics2 years ago
Politics2 years agoWho was Ebrahim Raisi and his status in Iranian Politics?
-

 Business2 years ago
Business2 years agoCarrectly: Revolutionizing Car Care in Chicago
-

 Sports1 year ago
Sports1 year agoKeely Hodgkinson Wins Britain’s First Athletics Gold at Paris Olympics in 800m
-

 Business2 years ago
Business2 years agoSaudi Arabia: Foreign Direct Investment Rises by 5.6% in Q1