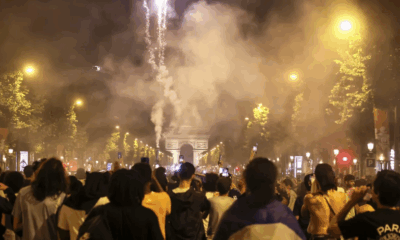News
WHO Calls on China for Transparency in COVID-19 Origins, Five Years After Pandemic Began
The World Health Organization (WHO) has reiterated its call for China to share critical data on the origins of COVID-19, marking five years since the pandemic’s first known cases emerged in Wuhan.
On December 31, 2019, the WHO’s China office reported a cluster of pneumonia cases in Wuhan, later identified as a novel coronavirus. Despite a lockdown imposed on the city of 11 million in January 2020, the virus had already spread globally, setting off a pandemic that claimed over seven million lives, overwhelmed healthcare systems, and devastated economies.
While much of the world has moved beyond pandemic-era restrictions, the origins of the virus remain an unresolved mystery. The lack of clarity has fueled scientific debate and geopolitical tension, with experts criticizing China for withholding crucial data.
“Understanding the origins of COVID-19 is a moral and scientific imperative,” the WHO said in a statement on Monday. “Without transparency, sharing, and cooperation among countries, the world cannot adequately prevent and prepare for future epidemics and pandemics.”
China has repeatedly defended its handling of the pandemic and the transparency of its data. Mao Ning, a spokesperson for China’s Foreign Ministry, stated Tuesday that China has actively supported global efforts to trace the virus’s origins and rejected accusations of political manipulation.
“China has shared the most data and research results on COVID-19 origin tracing and has made the greatest contribution to global research,” Mao asserted.
The origins of the virus remain hotly debated. Many scientists support the theory of a natural spillover, suggesting the virus jumped from infected animals to humans, possibly at Wuhan’s Huanan Seafood Market. However, some researchers endorse the lab-leak hypothesis, which posits the virus may have accidentally escaped from a research facility near the market.
Tensions surrounding the investigation have persisted since the pandemic’s early days. Western nations, including the United States, have accused China of withholding vital information, allegations Beijing denies. WHO officials have also criticized China for limiting access to data, with one official in 2023 calling the lack of disclosure “simply inexcusable.”
In 2023, WHO gained access to genetic sequences from samples collected at the Huanan market in early 2020. These sequences, later analyzed in the journal Cell, revealed the presence of coronavirus-susceptible animals in a specific market section but did not confirm direct animal-to-human transmission.
Reflecting on the pandemic’s impact, the WHO called for renewed commitment to learning from COVID-19. “As we mark this milestone, let’s honor lives lost, support those suffering from long COVID, and express gratitude to health workers who sacrificed so much,” the statement read.
News
Two Dead, Nearly 200 Injured as PSG Title Celebrations Turn Violent Across France
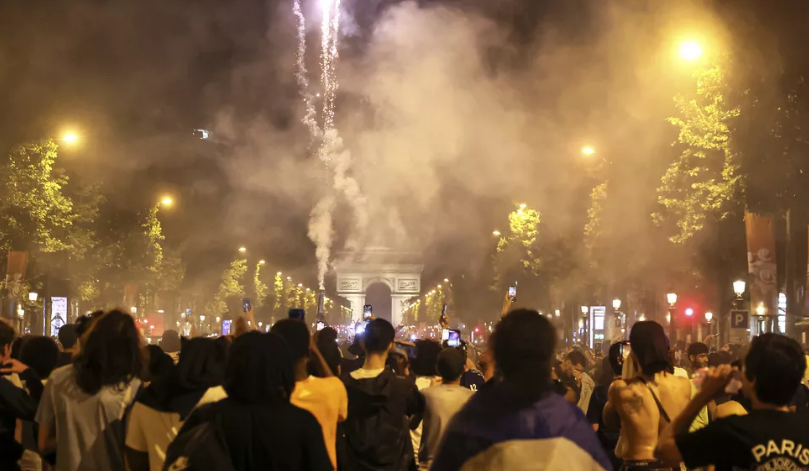

What began as jubilant celebrations of Paris Saint-Germain’s historic UEFA Champions League victory ended in violence and tragedy in parts of France, with two people killed and nearly 200 injured during street festivities that spiraled out of control.
Authorities confirmed on Sunday that a 17-year-old boy was fatally stabbed in the southwestern town of Dax during a PSG street gathering, while in Paris, a man died after his scooter was struck by a car amid the crowded celebrations. Both incidents are currently under investigation.
The unrest followed PSG’s dramatic win in Munich, where the club secured its first-ever Champions League title, marking a milestone in French football history. While fans across the country took to the streets to celebrate, several areas descended into violence.
According to the French Interior Ministry, a total of 294 people were arrested nationwide as of 2 a.m. Sunday. Of the nearly 200 injured, 21 were police officers—18 of them in Paris alone. One officer remains in a medically induced coma after being struck in the face by a firework.
Interior Minister Bruno Retailleau condemned the violence in a statement on social media. “True PSG fans are celebrating a magnificent achievement. Meanwhile, barbarians have taken to the streets to commit crimes and provoke law enforcement,” he said. “It is unacceptable that people cannot celebrate without being endangered by a violent minority.”
Despite the unrest, the majority of gatherings were peaceful, authorities noted, with large crowds celebrating the historic win in cities including Marseille, Lyon, and Lille.
The PSG squad returned to Paris from Munich on Sunday afternoon aboard a Qatar Airways charter flight, arriving at 4 p.m. The team is expected to continue celebrations in the capital with tens of thousands of fans, under heightened security measures.
The violent turn of events has reignited debate in France over crowd control during major sporting celebrations, and how best to ensure public safety without dampening national enthusiasm.
PSG’s Champions League triumph marks a defining moment for the club, which has long pursued European glory. As the team prepares for a hero’s welcome, officials are urging fans to celebrate responsibly and respect public safety.
News
Ukraine Launches Major Drone Assault on Russian Airfields, Hits Over 40 Strategic Bombers
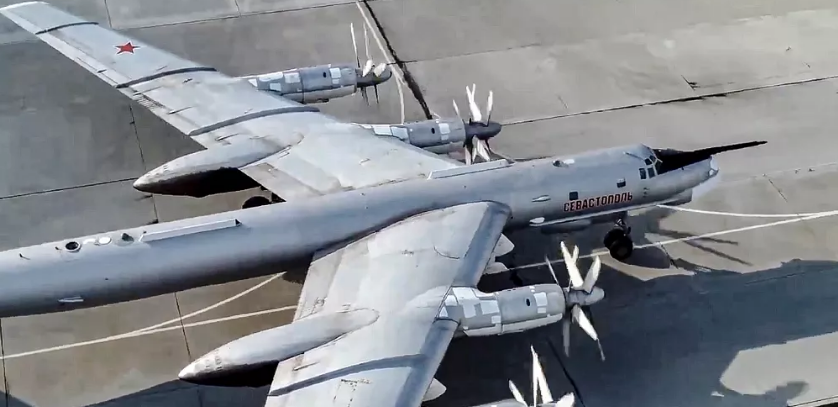

Ukraine’s Security Service (SBU) has claimed responsibility for a large-scale drone strike on four Russian air bases over the weekend, targeting dozens of strategic bombers across vast swaths of Russian territory — from Siberia to the Arctic.
According to Ukrainian officials, the operation, codenamed “Spiderweb” (Pavutyna), was launched on June 1 and struck 41 long-range bombers stationed at airfields in Russia’s Ryazan, Ivanovo, Irkutsk, and Murmansk regions. The attack is being hailed by Kyiv as one of its most ambitious and far-reaching strikes since the beginning of Russia’s full-scale invasion.
“Enemy strategic bombers are burning en masse in Russia,” a senior SBU official said, noting that the operation was specifically designed to cripple Moscow’s airstrike capabilities. “This is a large-scale special operation aimed at destroying enemy bomber aircraft.”
The four airfields targeted were Dyagilevo in the Ryazan region, Ivanovo in central Russia, Belaya air base in Irkutsk — over 4,000 kilometers from the front lines — and Olenya air base on the Kola Peninsula near the Arctic, roughly 2,000 kilometers from Ukraine’s border.
Ukrainian officials described the complex logistics of the operation, which involved covertly transporting drones deep into Russian territory, hiding them until the time of launch, and remotely executing the strikes. While specific details remain classified, Ukraine previously revealed it had developed drones with a flight range of up to 3,000 kilometers, enabling long-range operations like this.
Satellite imagery analyzed after the attack shows the presence of several high-value Russian aircraft types at the affected bases, including the Tu-95, Tu-22M3, Tu-160, and A-50 radar planes. These aircraft have been central to Russia’s long-range missile campaign against Ukraine.
The Tu-22M3, for example, is capable of carrying Kh-22 and Kh-32 cruise missiles at speeds exceeding Mach 4. The Tu-95, a Cold War-era bomber once designed to carry nuclear weapons, has been retrofitted to launch conventional cruise missiles. The A-50 aircraft provides airborne radar surveillance and target coordination for Russian forces.
The scale of the strike underscores Ukraine’s growing long-range capabilities and signals a shift in Kyiv’s strategy to disrupt Russian air operations at their source. President Volodymyr Zelenskyy said he had held meetings with the Ministries of Defense and Foreign Affairs, along with the General Staff and SBU, to coordinate further defense and counter-offensive planning.
There has been no immediate official response from Moscow regarding the extent of damage caused.
News
German Chancellor Merz to Meet President Trump in Washington Amid Global Tensions
-

 Business1 year ago
Business1 year agoSaudi Arabia’s Model for Sustainable Aviation Practices
-

 Business1 year ago
Business1 year agoRecent Developments in Small Business Taxes
-

 Politics1 year ago
Politics1 year agoWho was Ebrahim Raisi and his status in Iranian Politics?
-

 Business11 months ago
Business11 months agoCarrectly: Revolutionizing Car Care in Chicago
-

 Business11 months ago
Business11 months agoSaudi Arabia: Foreign Direct Investment Rises by 5.6% in Q1
-

 Technology1 year ago
Technology1 year agoComparing Apple Vision Pro and Meta Quest 3
-

 Politics1 year ago
Politics1 year agoIndonesia and Malaysia Call for Israel’s Compliance with ICJ Ruling on Gaza Offensive
-

 Sports10 months ago
Sports10 months agoKeely Hodgkinson Wins Britain’s First Athletics Gold at Paris Olympics in 800m