Health
Human Metapneumovirus Outbreak in China Sparks Global Attention
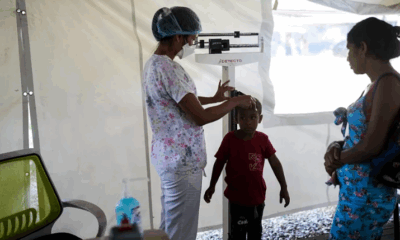
China is grappling with a surge in human metapneumovirus (HMPV) infections, adding to the global rise in respiratory illnesses this winter. While HMPV is a familiar virus, its outbreak highlights the challenges of managing respiratory diseases during the cold season.
Understanding HMPV
First identified in 2001 by Dutch scientists, HMPV is a common respiratory virus that infects most children by age five. It typically circulates in late winter or early spring and causes cold or flu-like symptoms such as cough, congestion, and shortness of breath.
For most, HMPV infections are mild and resolve within days. However, vulnerable groups, including infants, older adults, and individuals with weakened immune systems or chronic lung conditions, are at higher risk of severe illness requiring hospitalization.
In a study conducted in Italy during the 2018-2019 winter, 10-12% of patients infected with either HMPV or respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) required intensive care.
Current Outbreak in China
The outbreak in northern China has primarily affected children under 14, according to local health officials. Reports suggest that the combination of HMPV and influenza is straining healthcare systems in densely populated areas.
Experts note that the virus circulating in China has not mutated into a more dangerous strain. “China seems to be experiencing a severe HMPV season, much like overwhelming flu seasons we see in some years,” said Dr. Sanjaya Senanayake, an infectious diseases specialist at the Australian National University.
Impact Beyond China
Although the outbreak does not currently pose a global threat, other countries are seeing an uptick in HMPV cases. In England, test positivity rates for the virus increased from 2.29% in late November to 4.53% in December, suggesting wider spread.
Europe is also facing a “quad-demic” of respiratory illnesses, including influenza, COVID-19, RSV, and norovirus, straining healthcare systems across the continent.
Combating HMPV
Currently, there is no vaccine for HMPV, but several candidates are under development, including those targeting both HMPV and RSV. Experts have called for China to share data from its outbreak to aid vaccine research and global preparedness.
Preventative measures remain essential. Ventilating spaces, washing hands, and staying home when sick can reduce transmission. “The winter surge in infections is pushing many healthcare systems to the brink,” said Dr. Peter Openshaw, a respiratory expert at Imperial College London.
As respiratory illnesses continue to rise globally, vigilance and coordinated responses will be key to managing the burden on public health systems.
Health
Europe Pays Less for Medicines Than the U.S., but Prices Still Vary Widely by Country
Health
Global Nurse Shortage Worsened by European Reliance on Foreign Healthcare Workers, WHO Warns
Health
Early-Onset Cancer Rates Rising in U.S., But Deaths Mostly Stable, Study Finds

A new U.S. government study has revealed that while cancer diagnoses among people under 50 are on the rise, the overall death rates for most types of cancer in this age group remain stable.
Published Thursday in the journal Cancer Discovery, the study is one of the most comprehensive assessments to date of early-onset cancers, analyzing data from more than two million cases diagnosed in Americans aged 15 to 49 between 2010 and 2019.
The findings show that 14 out of 33 cancer types had increasing incidence rates in at least one younger age group. The most significant increases were seen in breast, colorectal, kidney, and uterine cancers. Women accounted for about 63 percent of the early-onset cases.
“This pattern generally reflects something profound going on,” said Tim Rebbeck of the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, who was not involved in the study. “We need to fund research that will help us understand why this is happening.”
The study found that, compared to 2010 data, there were 4,800 more breast cancer cases, 2,000 additional colorectal cancers, 1,800 more kidney cancers, and 1,200 extra uterine cancers by 2019.
Despite the rising numbers, researchers emphasized a key reassurance: death rates for most of these cancers are not increasing. However, exceptions were noted—colorectal, uterine, and testicular cancers saw slight rises in mortality among younger adults.
The causes behind the rise in early-onset cancers are not fully understood. The study’s datasets do not include information on potential risk factors such as obesity, lifestyle, or access to healthcare. However, researchers, including lead author Dr. Meredith Shiels of the National Cancer Institute, highlighted obesity as a possible driver.
“Several of these cancer types are known to be associated with excess body weight,” said Dr. Shiels. She also pointed to advances in detection and changing screening practices as possible contributors to earlier diagnoses.
Breast cancer trends may also be influenced by shifting reproductive patterns, such as women having children later in life, which has been associated with increased cancer risk due to fewer years of pregnancy and breastfeeding—factors known to lower risk.
Not all cancer types followed the upward trend. Rates of more than a dozen cancers, including lung and prostate cancer, are decreasing among younger people. Researchers attribute the lung cancer decline to reduced smoking rates, while updated PSA screening guidelines are likely behind the drop in prostate cancer diagnoses.
Experts plan to convene later this year to further investigate the growing early-onset cancer burden and explore targeted prevention strategies.
-

 Business12 months ago
Business12 months agoSaudi Arabia’s Model for Sustainable Aviation Practices
-

 Business12 months ago
Business12 months agoRecent Developments in Small Business Taxes
-

 Politics12 months ago
Politics12 months agoWho was Ebrahim Raisi and his status in Iranian Politics?
-

 Business10 months ago
Business10 months agoCarrectly: Revolutionizing Car Care in Chicago
-

 Business11 months ago
Business11 months agoSaudi Arabia: Foreign Direct Investment Rises by 5.6% in Q1
-

 Technology12 months ago
Technology12 months agoComparing Apple Vision Pro and Meta Quest 3
-

 Politics12 months ago
Politics12 months agoIndonesia and Malaysia Call for Israel’s Compliance with ICJ Ruling on Gaza Offensive
-

 Sports9 months ago
Sports9 months agoKeely Hodgkinson Wins Britain’s First Athletics Gold at Paris Olympics in 800m